Arthritis Treatment
Arthritis is a general term used to describe inflammation of the joints, and it can affect one or multiple joints. There are many types of arthritis, but the two most common forms are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
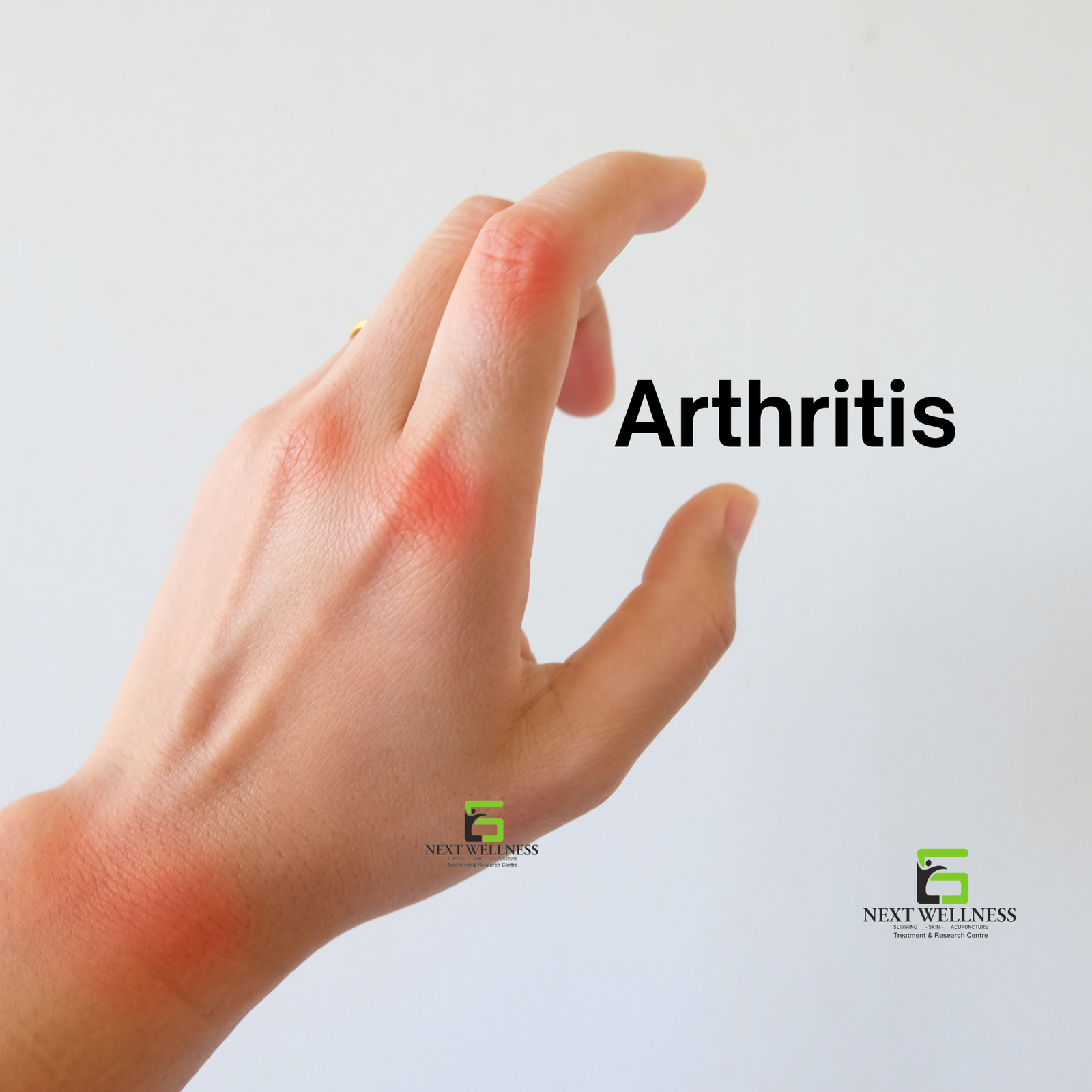
There are many types of arthritis, but the two most common forms are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
1. Osteoarthritis (OA):
Cause: Osteoarthritis is often a result of wear and tear on the joints over time. It can also occur due to joint injuries, obesity, or a genetic predisposition.
Symptoms:
– Pain and stiffness in the affected joint, particularly after periods of inactivity.
– Limited range of motion.
– Joint swelling and tenderness.
– Grating sensations (crepitus) during joint movement.
Treatment:
acupuncture
– Pain medications.
– Physical therapy and exercise.
– Weight management.
– Assistive devices (e.g., braces or canes).
– Joint injections with corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid.
– In severe cases, joint replacement surgery.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
Cause: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks the joints, leading to inflammation.
Symptoms:
– Joint pain, swelling, and stiffness.
– Symmetrical joint involvement (often affecting joints on both sides of the body).
– Fatigue and weakness.
– Rheumatoid nodules (lumps under the skin).
– Morning stiffness that lasts for extended periods.
Treatment:
– Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow down the progression of the disease.
– Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain and inflammation.
– Corticosteroids for short-term symptom relief.
– Biologics, a newer class of drugs targeting specific components of the immune system.
– Physical therapy and exercise.
– Joint replacement surgery in severe cases.
Other Types of Arthritis:
– Psoriatic Arthritis: A form of arthritis associated with psoriasis, an autoimmune skin condition.
– Ankylosing Spondylitis: A type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints.
– Gout: A form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints.
– Lupus Arthritis: Associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, an autoimmune disease affecting multiple organs.
Lifestyle Recommendations:
– Regular Exercise: Low-impact exercises help maintain joint flexibility and strengthen surrounding muscles.
– Healthy Diet: Maintaining a healthy weight and consuming a balanced diet can help manage arthritis symptoms.
– Joint Protection: Avoiding excessive strain on the joints and using assistive devices when needed.
– Medication Management Adhering to prescribed medications and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers.
It’s crucial for individuals experiencing joint pain, stiffness, or other symptoms suggestive of arthritis to seek medical evaluation. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend an appropriate treatment plan based on the specific type of arthritis and its severity. Early intervention and management are essential for minimizing joint damage and improving overall quality of life.
